Inflammation is a term that many people link with symptoms such as pain, swelling, or discomfort. However, it is a lot more intricate than that. In fact, it is one of the main ways that your body is able to recover and protect itself from damage. Nevertheless, the situation becomes dangerous when it is not controlled.
Knowing its mechanism, identifying the triggers, and being able to control it are the things that can help your inflammation health in the long run.
The body's immune system reacts with it. Your immune system sends help to the injured area once the signals for it are received. Fighting cells are the first to arrive and the most aggressive; they often are. They release various chemicals that kill enemies, such as bacteria or viruses. As a result of this process, the skin around the infection becomes red, warm, and swollen, which are the symptoms recognized by everyone.
It is basically a system that allows the body to cope with injuries and infections. The main aim of this protective reaction is to do away with pathogens, repair injuries and bring back the regular function.
It is of two major categories:
It is characterized as an abrupt one and has a very short duration. For instance, if you have a sprained your ankle, swelling and pain are some of the symptoms of the recovery process that you experience.
It is long-term and has a tendency to turn harmful. It can be there without an obvious injury or infection. The constant alarm situation that this entity is in can, over time, cause a whole range of diseases.
Acute inflammation is a major contributor to our well-being. It is the body's inherent healing mechanism, the system that is always in operation, though it does not show itself very much.
For example:
In all these instances, it is good. They are brief and switch off when the task is completed. Without them, injuries would take longer to heal and infections would spread rapidly.
Problems arise when the infection does not turn off. Chronic inflammation is a term used to describe a persistent, low-grade inflammatory reaction that causes damage to your tissues and organs gradually and at a very slow rate. This condition is frequently referred to as the “silent killer” because it progresses without symptoms but is responsible for a variety of serious health conditions, such as:
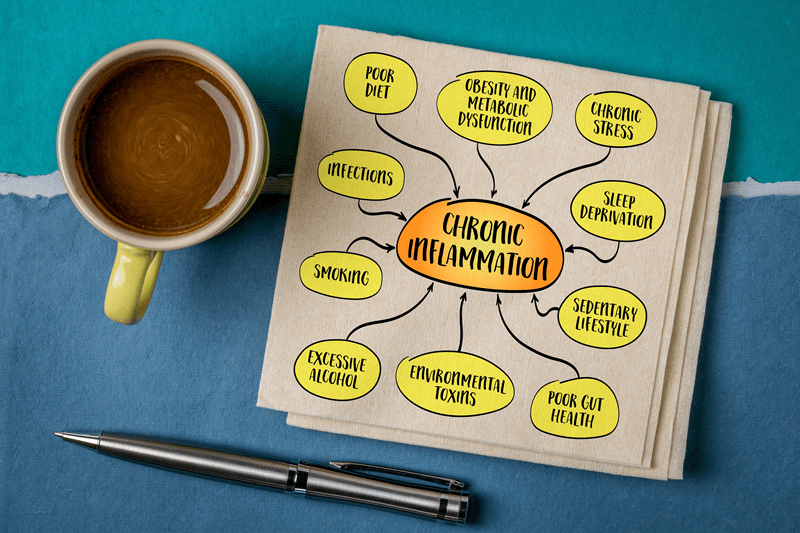
Knowing what causes it is the main thing needed to be able to control it properly. Short-term inflammatory reactions resulting from injuries, infections, or other causes are easy to understand and identify; however, chronic inflammatory reactions are a bit more complicated since they result from various factors that relate to lifestyle, living conditions, etc. Some of its causes are:
Some autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, are characterized by immune attacks on the body’s own healthy tissues, which in turn leads to a persistent inflammatory reaction.
One of the most influential factors in managing it is diet. It is because some foods have the ability to provoke it, while others soothe it. When on the right diet, it is almost as if you are giving your body natural medicine.
Some of the foods that can help you down are:
Meanwhile, to lower it, dietary intake of sugary beverages, deep-fried snacks, and processed meats should be kept to a minimum, if not completely; these types of consumption can lead to worse outcomes and make the coexisting health problems severe in the long run.
Apart from diet, certain lifestyle habits can have a great impact on your inflammatory condition. Small personal changes to your daily routine will be effective in this case.
Here are some effective habits to implement in your life:
A moderate kind of sport activates your immune system, and a decrease in inflammatory markers can be observed. So, sessions of brisk walking, swimming, or yoga would be very beneficial to you.
Try to sleep well for at least 7–8 hours per night. The body during this period of time it is supposed to be the repair of the tissues and it is elongating the stress-related inflammatory reaction.
Certainly, chronic stress is one of the major causes of high inflammatory reaction levels. Consider meditation, deep breathing, or even hobbies to relax and destress.
Smoking and excessive drinking are the main causes that lead to it, and they can be the reason for the worsening of numerous diseases.
One of the things that is very helpful in removing the waste matter is water, and at the same time, it is very refreshing for the body’s normal functions of healing.
These are not very complicated, but these very acts will have an impact on how the body will respond to the inflammatory reaction that is present.
It is not always that you can feel its presence in your body, but your body delivers you certain signals that can be identified as chronic inflammation. Symptoms might be:
If you are regularly encountering these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Together with the doctor, you can decide on some blood examinations to check for certain markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), that indicate the levels of inflammatory reaction in the body.
An inflammatory reaction could be considered both a friend and a foe. In its correct form, it is necessary for the healing process. Yet, if it becomes chronic, it slowly but surely adds to illness and discomfort. Hence, being able to distinguish between them is your body’s way of granting you the ultimate balance keeper role.
By knowing what sets off and how to soothe it, you can gain control over your condition and encourage the body to heal and flourish on its own.
This content was created by AI